Sand washing plants are used to produce clean fine aggregate for use in multiple applications. These plants consist of processing equipment designed for sizing, washing, classifying, scrubbing and/or dewatering sand to meet specific goals.
Some common types of sand plants are:
- Construction sand plants for producing concrete and mason sand
- Frac sand plants
- Industrial sand plants for producing sand for glassmaking, foundries, filtration, ceramics and more
- C&D recycling plants
- Modular plants
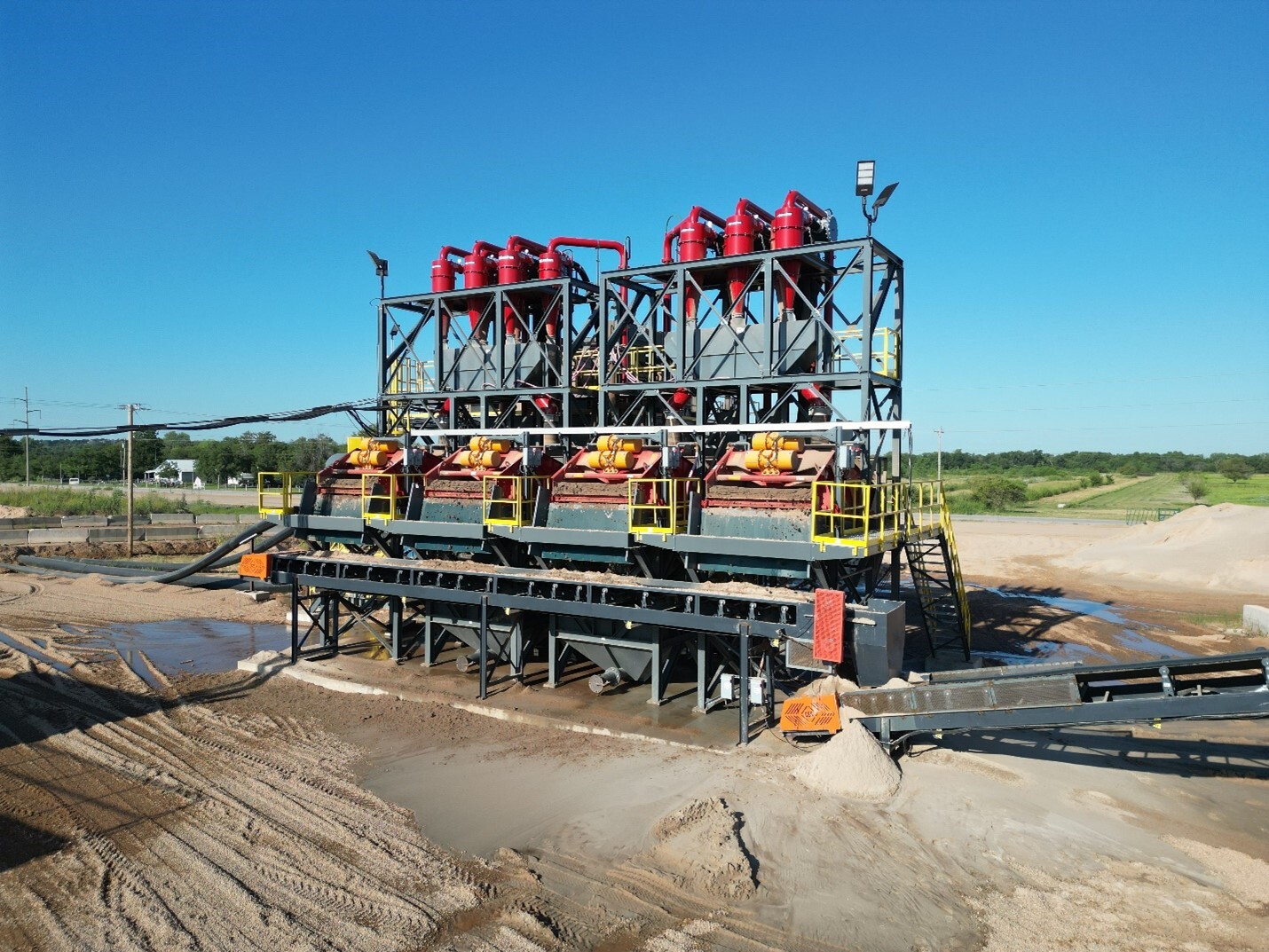

Construction sand plants
Wash plants designed for producing construction sands, such as concrete and mason sand, typically include one or more of the following equipment types:
- Sand Classifying Tank
- Fine Material Screw Washer
- Hydrocyclone/Separator™
- Dewatering Screen
- Flat Bottom Classifier
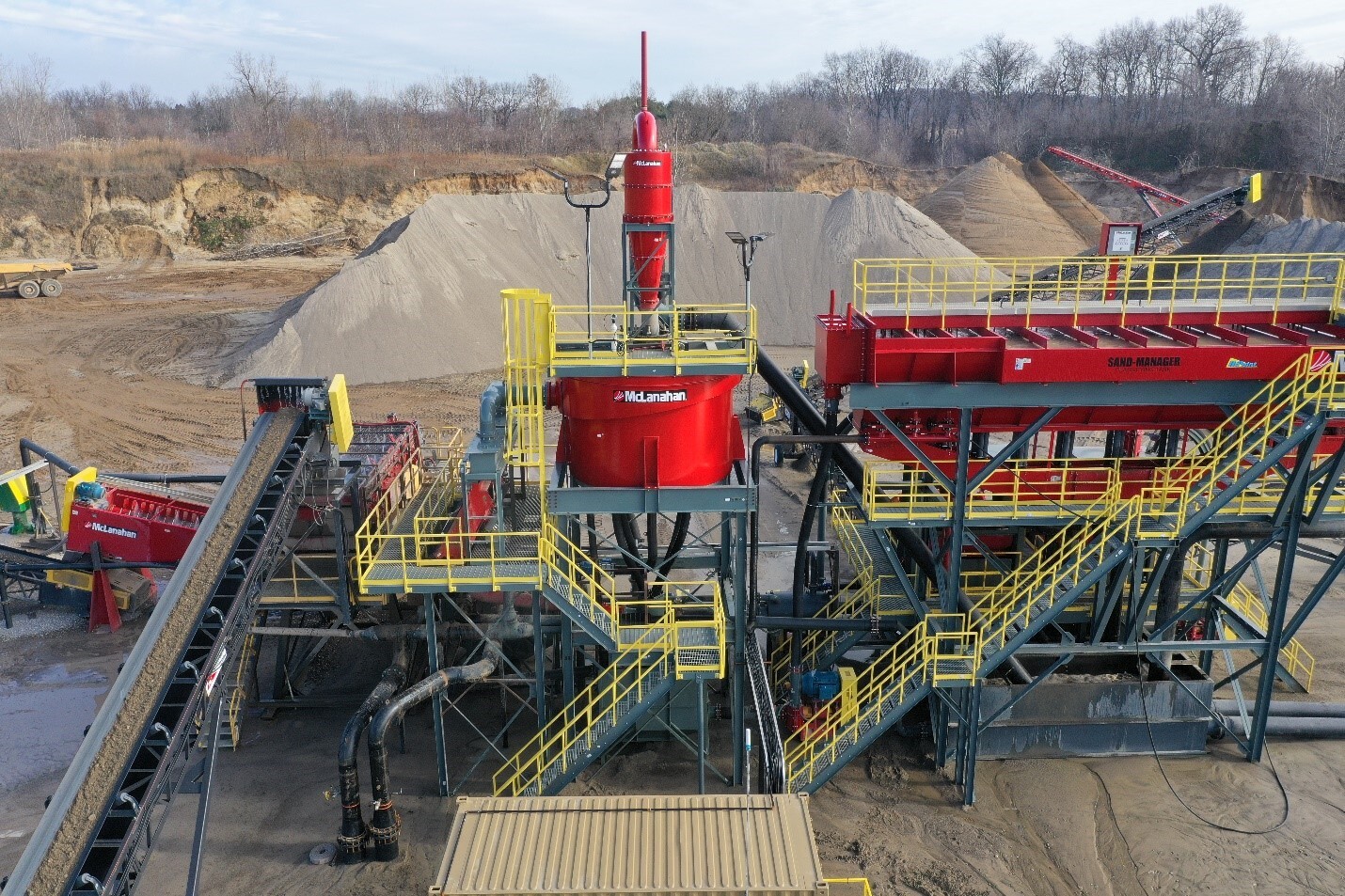
Sand Classifying Tanks are used to scalp off excess water, create multiple products from a single feed stream and remove excess fines. These machines are unrivaled for handling deposits that have a belly of excess material or lack of a certain size because they can classify material where the producer wants it to go, either in the product(s) or out to waste.
A disadvantage of Sand Classifying Tanks is they are big, so they have a large footprint. Sand tanks also discharge material in a slurry around 30-40% solids, so additional dewatering equipment is necessary to create a conveyable product.
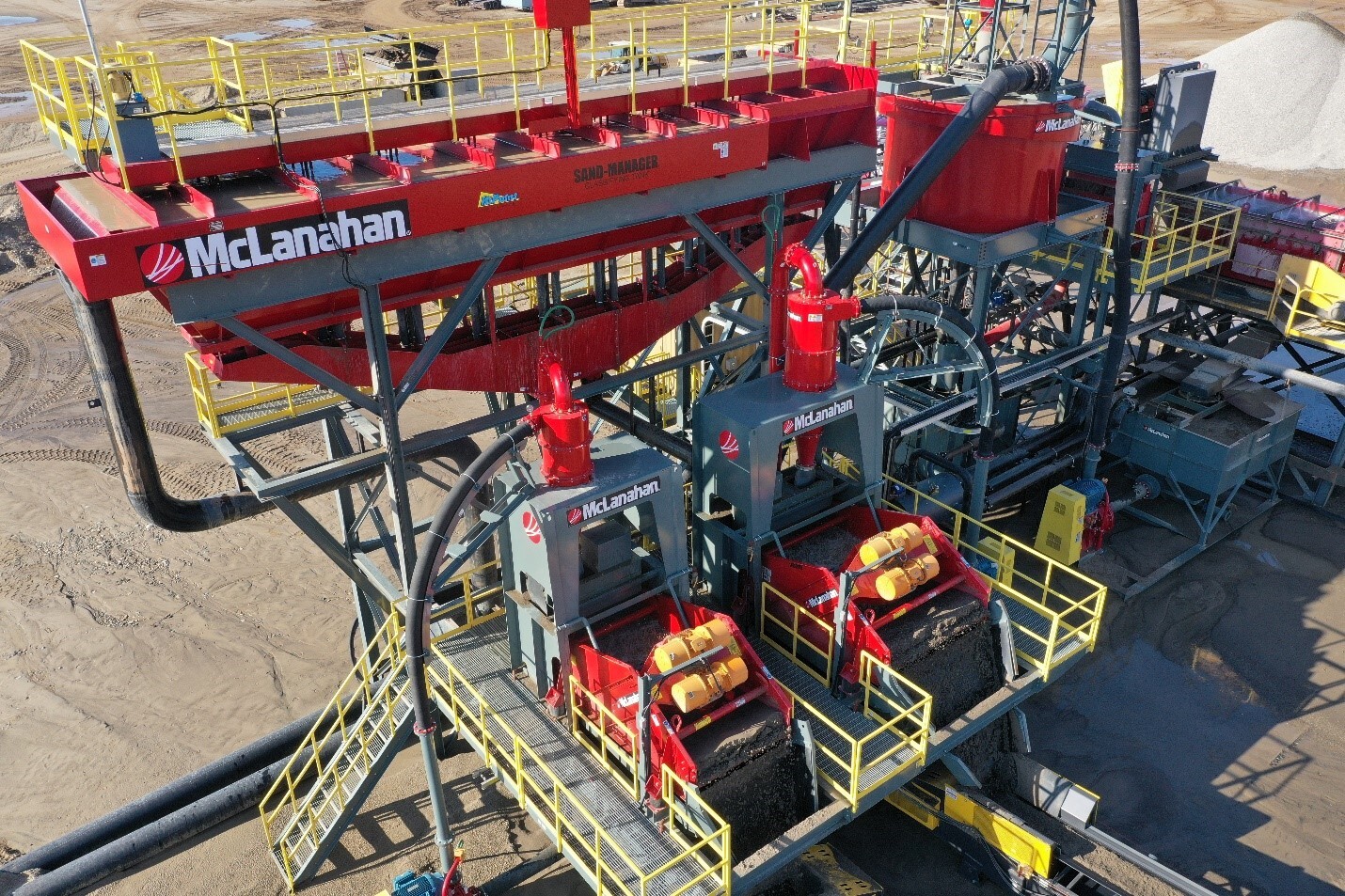

Traditionally, Fine Material Screw Washers have been used to dewater sand tank underflow to a stackable state, but Hydrocyclones/Separators™ and Dewatering Screen combinations are also a popular choice. Dewatering Screens are sometimes added after Fine Material Screw Washers used for dewatering sand tank underflow to reduce the moisture content even further ahead of stockpiling.
Fine Material Screw Washers are often used as a standalone sand washing solution, providing the functions of washing, classifying and dewatering in a single machine. They’re popular for many reasons, namely that they’re well known, easy to operate and are flexible enough to handle fluctuations in the feed.
However, this flexibility can also be the cause of inefficiency, which is often a criticism of screw washers. Screw washers can be efficient machines when operated correctly within their design parameters.
If looking to improve the efficiency of screw washers, Hydrocyclones/Separators™ can be added to the process in strategic ways. Feeding a screw with a Hydrocyclone/Separator™ can provide a double-wash, removing fines and slimes ahead of the screw washer for a cleaner product. If you’re losing too many good fines to waste, Hydrocyclones/Separators™ can be used to recover product-sized fines from the overflow and discharge them back onto the dry deck area of the screw.
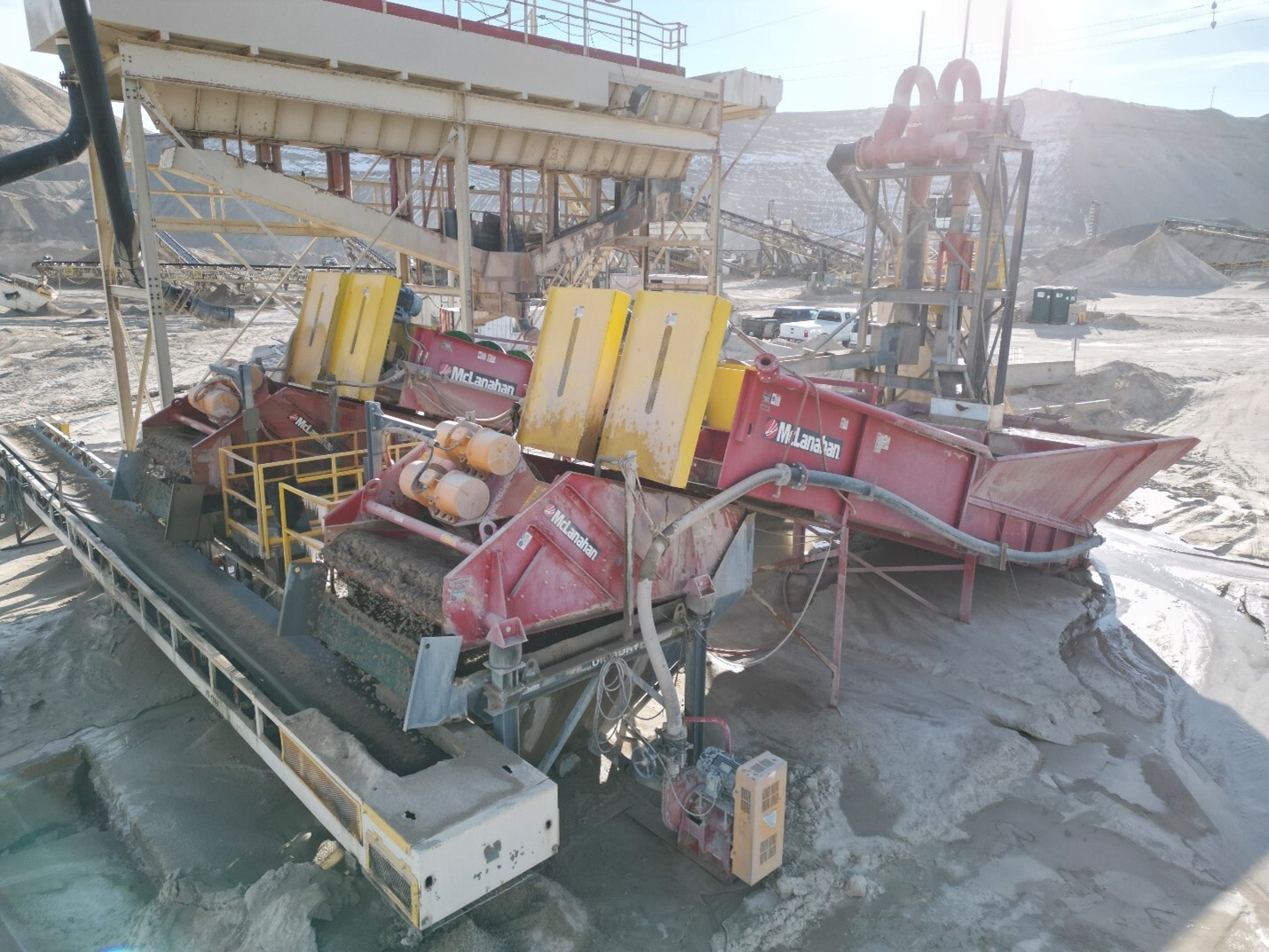

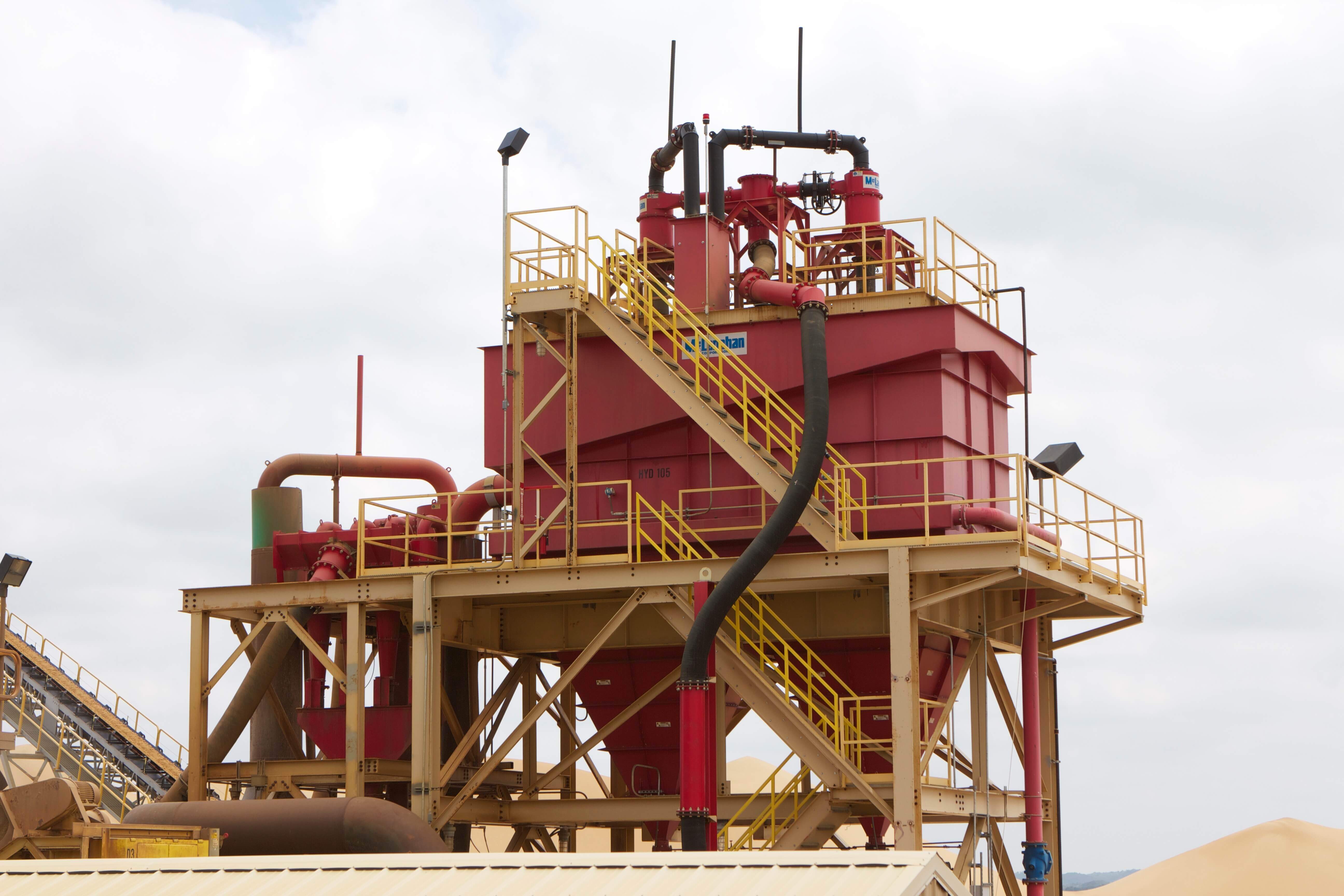
Hydrocyclones/Separators™ can be used for many functions within a sand washing plant. In addition to providing a double wash and recovering product-sized fines, these highly efficient devices can be used to deslime and dewater feeds ahead of a sand tank. They can also be used in conjunction with Dewatering Screens for the primary washing of sand, providing a more compact wash plant with a smaller footprint. While Hydrocyclones/Separators™ have no moving parts, they need a Slurry Pump to provide material feed and flow rate, which requires more horsepower to operate than a screw.
Dewatering Screens are another versatile piece of wet processing equipment. They are used for dewatering material to a drip-free state. Dewatering Screens can be used in conjunction with Fine Material Screw Washers to improve product moisture from around 20% with a screw alone to as low as 7%, depending on the material. They are commonly combined with Hydrocyclones/Separators™ to dewater sand tank underflow or for the primary washing and dewatering of sand.

Regardless of the application, Dewatering Screens will discharge a material that is drip-free. This has many advantages, the biggest of which is quicker sale. Less water in the product means less water leaching out of stockpiles, less water being transported in the final product and better housekeeping on site. Reduced moisture in the final product can also allow for less conveyor maintenance, as drier sand doesn’t stick as readily to conveyor belts and return rollers, and less mess underneath conveyors.
Another common piece of processing equipment used in the production of construction sand is Flat Bottom Classifiers. Flat Bottom Classifiers excel at removing lignite and other light organics from sand feeds that can be detrimental to the final product.

Construction sand specifications can vary from region to region and even producer to producer. This, coupled with variations in feed deposits and feed characteristics, means that what sand washing plant is best for one producer may not be what is best for another. Using a combination of washing and classifying equipment, such as Classifying Tanks, Fine Material Screw Washers, Hydrocyclones/Separators, Dewatering Screens and Flat Bottom Classifiers in various configurations allows producers to achieve their goal of a clean, in-spec sand product.
Frac sand plants
Frac sand is used in hydraulic fracturing (fracking) to prop open the fissures that release oil and natural gas to the surface. To withstand this extreme pressure and allow the oil and gas to flow, sand must meet strict specifications in size, shape and strength. The best sand for fracking is a high-quality silica sand that is spherical in shape and uniform in size.
Frac sand washing plants include equipment in various configurations designed to meet specific goals. Frac sand plants can be as simple as a Hydrocyclone for making the desired mesh cut and a Dewatering Screen for reducing the moisture content in the final product or they can include multi-stage classification and attritioning cycles depending on the nature of the deposit and the final product requirements.

Many frac sand washing plants include hindered settling classifiers such as Hydrosizers™. Hydrosizers™ are the most efficient wet classification equipment and are capable of providing sharp cuts required for frac sand. They are typically fed by a Hydrocyclone to deslime or remove excess fines ahead of classification.
Attrition Cells/Scrubbers also play an important role in the production of frac sand. These machines provide a heavy-duty scrub of sand particles to not only remove stubborn stains and coatings, but also to improve the turbidity and durability of the sand.
Durability is a measure of how sand particles will resist breaking down over time. Sand with high durability is necessary for fracking so that the grains don’t break down in the well and cause the fissures to collapse.
Turbidity is a measure of suspended particles in water; essentially it is a measure of how dirty the sand is. Clean sand with low turbidity is essential for fracking.
Attrition Cells improve the durability of sand by separating clusters of particles and/or fractured particles that may be strong enough to pass through sizing process but will break down once under stress. Attrition Cells can improve the turbidity of sand by removing persistent coatings and clays.
Once the frac sand has been sized and washed, Dewatering Screens can be used to remove excess moisture ahead of the drying process.

Industrial sand plants
Industrial sand, used for ceramics, filtration, foundries, glassmaking, recreation and more, is characterized by shape, size, color, crush resistance and chemistry. Industrial sand washing plants are designed for sizing, classifying, desliming, scrubbing and dewatering the sand so that it meets the desired specifications.
Typical equipment used in industrial sand washing plants include:
- Hydrocyclones for desliming the feed ahead of classification
- Hydrosizers™ or Hydrocyclones for making the desired cut
- Attrition Cells for scrubbing the sand to remove stains, coatings and pretend particles to improve turbidity and durability
- Dewatering Screens, Separators™ or Fine Material Screw Washers for reducing the moisture content ahead of the next stages in the production process
C&D recycling plants
C&D recycling plants recover aggregate material from construction and demolition (C&D) debris streams. Typical C&D debris consists of bulky inert waste materials such as brick, concrete, asphalt, soil, metals, sand, stone and other building materials. C&D recycling plants separate out the valuable aggregate and process it for reuse in the construction industry, allowing producers to reclaim aggregates that would otherwise be sent to landfills. Washing is an integral part of this repurposing stage to increase the value of the recycled aggregate as well as allow it to be used in a wider range of applications.

Wash plants processing recycled aggregate include much of the same equipment as construction sand washing plants because the goal of producing clean, in-spec material is the same. However, a few considerations must be taken into account given the nonhomogeneous and unpredictable nature of C&D debris streams.
In addition to sizing, washing, classifying, scrubbing and dewatering equipment, recycled aggregate plants typically include scalping stages at the beginning of the process to remove large metals and other debris that can damage processing equipment. When processing hydrovac waste, a scalping stage at the beginning of the process removes excess water inherent to this type of feed.
Overband magnets and eddy current separators are also key pieces of equipment in recycled aggregate plants for removing small ferrous and non-ferrous metals at various stages of the process, including ahead of washing/classifying equipment and ahead of stockpiling.
Configurations of recycled aggregate plants vary depend on the type of material being processed and how it arrives on site.
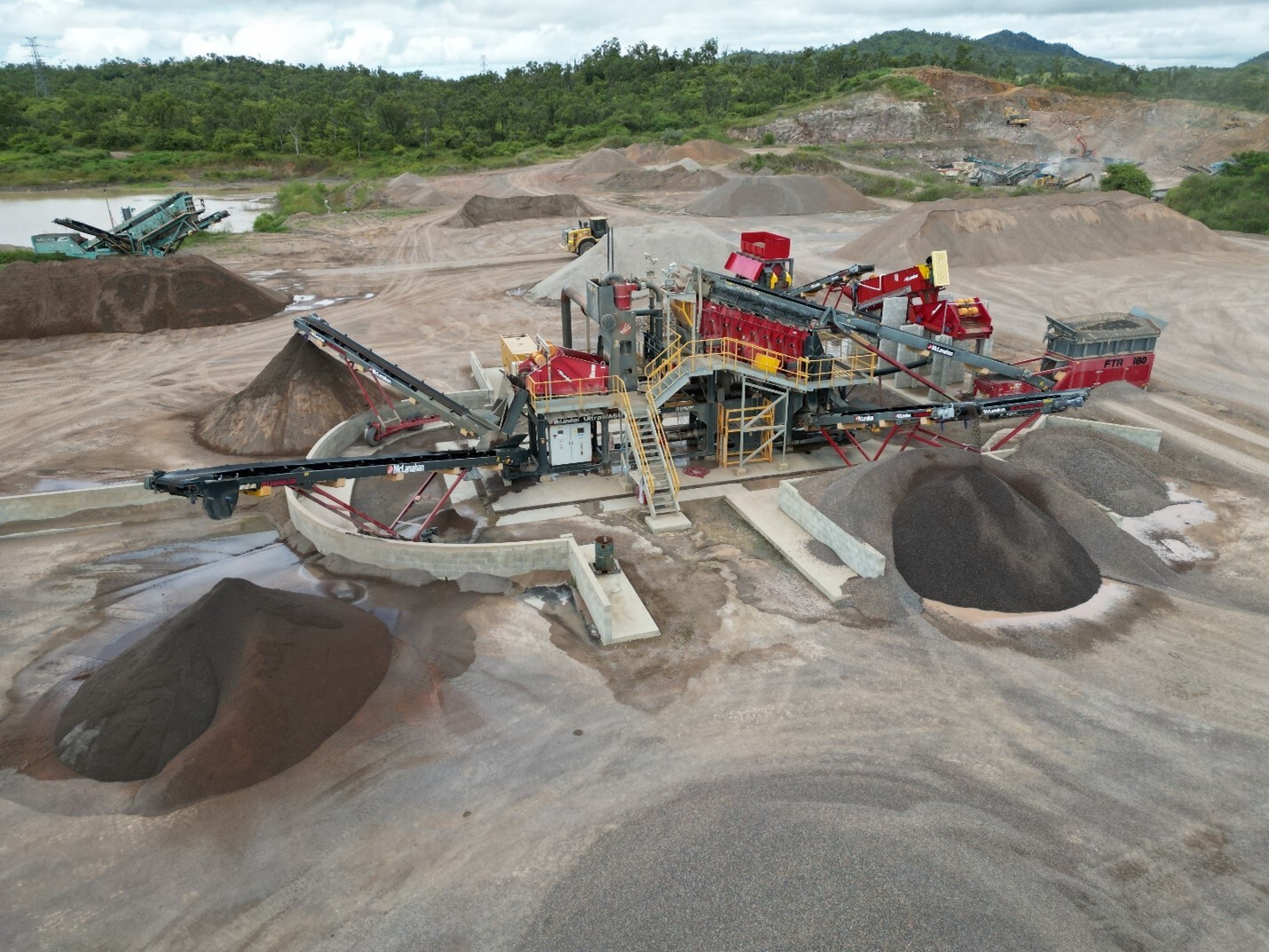
Modular wash plants
Modular sand washing plants are compact systems designed to be readily available and easy to install. These skid-mounted plants are composed of standardized pieces of equipment that can be assembled, disassembled, relocated or reconfigured to meet the changing needs of the site. Modular sand plants are often more cost effective and consist of screening, washing, classifying and scrubbing modules that can be configured a number of ways to achieve the desired outcome.

Water recycling and tailings management
All sand washing plants use water to clean aggregate, producing a waste stream of deleterious material and process water. Traditionally, the waste stream is pumped to settling ponds, which can be expensive and time consuming to maintain.
Producers should consider how tailings management and water recycling equipment, such as Ultra Fines Recovery Plants, Thickeners, Centrifuges and Filter Presses, can help them improve their operation. This equipment can be used to recycle immediately reusable process water and reduce the volume of material reporting to settling ponds, potentially eliminating the need for settling ponds altogether. In some instances, the solids material recovered from the waste stream can be sold as a byproduct or used on site for backfill.

Every sand washing application is unique, so it is important to consider your deposit and your desired production goals when determining what equipment configuration is best. It is also important to consider other things such as available footprint and operational and maintenance costs when evaluating a solution. Sometimes, more than one solution may be available, so equipment preference can also be a contributing factor.